This article is for an older version of HandBrake. All versions.
Dieser Artikel ist für eine ältere Version von HandBrake. Alle Versionen.
Adjusting quality
HandBrake’s default settings and most of the official Presets use a constant quality encoding method. This makes your new video look consistent from start to finish. Always use constant quality unless you have a specific reason not to.
You can use the default setting for the Preset you selected, or adjust the quality control higher or lower depending on your tastes. Increasing quality will make your new video take up more space on your computer or playback device, whereas reducing quality will typically make your new video take up less space.
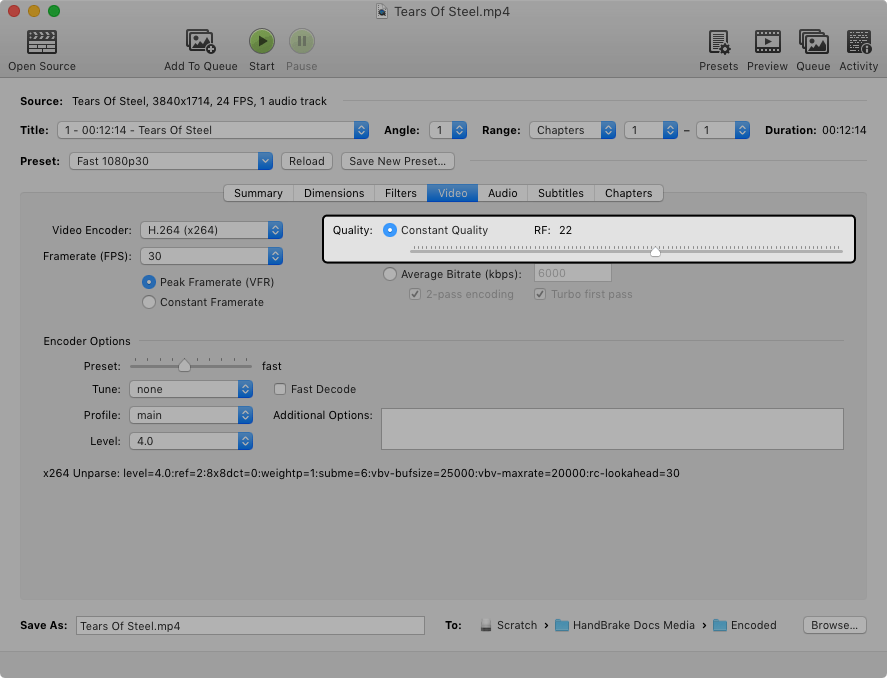
Using the quality control
On the Video tab, increase video quality by adjusting the control toward the right, and reduce video quality by adjusting the control toward the left. Begin by making small adjustments; plus or minus a few steps is usually noticeable.
You can test your settings by encoding and watching short clips using HandBrake’s Preview feature.
Recommended quality settings
Recommended settings for the x264 and x265 encoders:
- RF 18-22 for 480p/576p Standard Definition1
- RF 19-23 for 720p High Definition2
- RF 20-24 for 1080p Full High Definition3
- RF 22-28 for 2160p 4K Ultra High Definition4
Recommended settings for the SVT-AV1 encoder:
- RF 22-32 for 480p/576p Standard Definition
- RF 25-35 for 720p High Definition
- RF 25-35 for 1080p Full High Definition
- RF 25-40 for 2160p 4K Ultra High Definition
For other encoders, start with a value in the middle of the scale, and adjust in small increments as desired.
These values may seem counterintuitive at first, but the reasoning is simple and easy to demonstrate in practice. When encoding higher resolution content, you have more information to work with. Therefore, you can get away with using lower quality values than you can with lower resolution content, as any loss is a smaller percent of the whole, and ultimately less perceptible.
Raising quality by a few steps may produce better results when encoding animated Sources (anime, cartoons). Lower quality settings may be used to produce smaller files. Drastically lower settings may show significant loss of detail.
Using higher than recommended quality settings can lead to extremely large files that may not be compatible with your devices. When in doubt, stick to the recommended range or use the default setting for the Preset you selected.
Differences between encoder quality scales
Most of HandBrake’s official Presets use the x264, x265, or SVT-AV1 video encoders with a Constant Rate Factor, sometimes abbreviated CRF or simply RF. For these encoders, a lower RF number produces higher quality video, and a higher RF number produces lower quality video. This is reversed for other encoders, such as Apple VideoToolbox, where a higher number produces higher quality. In all cases, adjusting HandBrake’s quality control to the right always increases quality, and adjusting the control to the left always decreases quality.
Even where the quality scale is similarly labeled, quality values are not comparable between encodes across multiple encoders. You should not expect an x264 encode at RF 25 to be similar to an x265 encode at RF 25 or an SVT-AV1 encode at RF 25, as each encoder’s quality scale corresponds only to its own internal rate control method, and these are three separate encoders corresponding to three different video coding standards.
Display size and viewing distance
Imperfections tend to be more noticeable at larger display sizes and closer viewing distances. This is especially true for lower resolution videos (less than 720p), which are typically scaled or “blown up” to fill your display, magnifying even minor imperfections in quality.
You may wish to slightly increase quality for viewing on larger displays (50 inches / 125 cm diagonal or greater), or where viewing from closer than average distances5. Reduced quality may be acceptable for viewing on smaller screens or where storage space is limited, e.g. mobile devices.
Next steps
Continue to Previewing your settings.
- SD video has a resolution of 720x480 or fewer pixels (720x576 for PAL). DVDs, small web videos, and most analog sources are SD.↩
- 720p HD video has a resolution of 1280x720 pixels. With three times the resolution of SD, and about half that of 1080p HD, 720p HD is commonly used by consumer video cameras, web videos, and broadcast TV sports.↩
- 1080p HD video has a resolution of 1920x1080 pixels—twice the resolution of 720p and six times the resolution of 480p. 1080p HD video is commonly used by mobile phones and tablets, consumer and professional video cameras, and Blu-ray.↩
- 2160p UHD video has a resolution of 3840x2160 pixels and is four times the resolution of 1080p. 4K video is used by high-end mobile phones and tablets, consumer and professional video cameras, and 4K Blu-ray.↩
- Learn more about optimum viewing distances for high definition TV displays.↩